How VIDIZMO Processes Content for AI, Search, and RAG
VIDIZMO Content Processing is the foundation of the platform's AI-powered search, analytics, and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) capabilities. It transforms raw content files that include video, audio, images, and documents into structured, searchable data.
This processing layer extracts transcripts, visual text, metadata, and AI insights that downstream systems use to generate embeddings, enable hybrid search, and power conversational AI experiences.
This article explains how content flows through the VIDIZMO content processing layer, what outputs are produced, and how those outputs enable AI-driven discovery and RAG scenarios.
Architecture at a Glance
VIDIZMO uses a layered processing architecture:
-
Content Processing: Extracts AI insights from processed content.
-
Content Embeddings: Converts processed outputs into semantic vectors.
-
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): Uses retrieved content to ground AI responses.
This article focuses on Content Processing, which produces the structured outputs used for keyword search (transcripts, OCR text), and serves as the foundation for embedding generation and semantic search capabilities.
Content Processing Workflow
The content processing layer handles the initial ingestion and AI analysis of uploaded content. This stage extracts the raw textual and visual information that will later be converted into embeddings.
The following diagram illustrates the end-to-end content processing workflow within VIDIZMO.
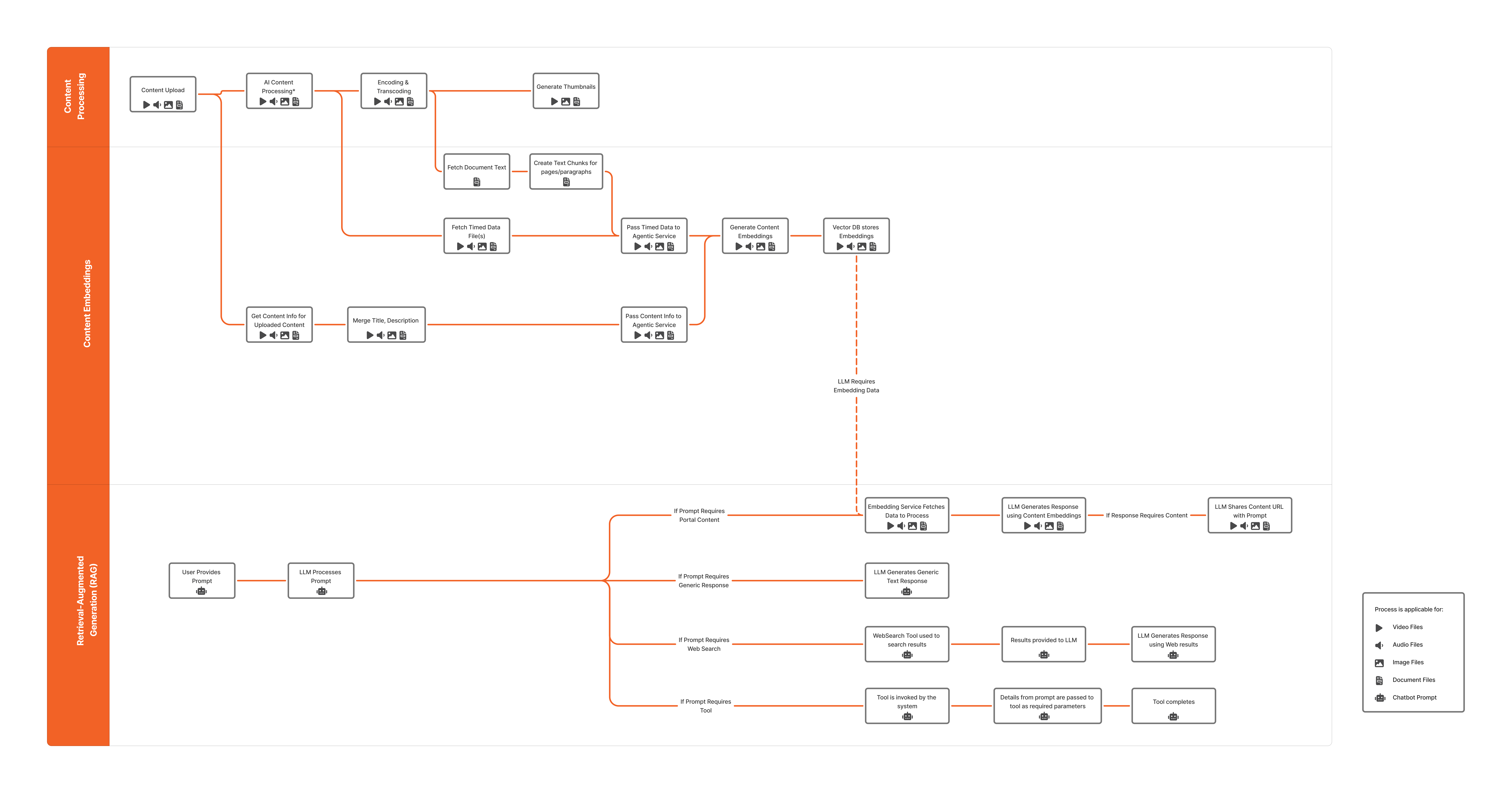
Content processing in VIDIZMO converts raw content into structured AI insights used by the Content Embeddings and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) layers.
Rather than operating on raw video, audio, images, or documents, VIDIZMO’s AI systems rely on processed outputs generated earlier. These outputs include normalized text, metadata, and semantic signals that provide authoritative context for downstream AI workloads.
AI Content Processing
As shown in the diagram above, content processing begins when a user uploads media to the VIDIZMO platform and includes the following stages:
- Content Upload: Ingestion of video, audio, image, and document files.
- Transcoding and Encoding: Conversion to standardized formats for playback and analysis.
- AI Insights: Extraction of transcripts, OCR text, video descriptions, and object detection results.
- Thumbnail Generation: Creation of preview images for navigation.
For detailed information about each AI processing workflow, see AI Content Processing in VIDIZMO.
Pre-Embedding Data Preparation
Before embeddings can be generated, VIDIZMO prepares content outputs for vectorization:
- Fetch Timed Data: Retrieves time-coded transcripts, captions, and video descriptions from audio and video content.
- Fetch Document Text: Extracts text content from documents and OCR outputs.
- Create Text Chunks: Splits large text bodies into embedding-ready segments, preserving semantic boundaries and applying overlap for context continuity.
These preparation steps ensure that downstream embedding generation receives clean, structured text optimized for vector representation.
Content Embeddings
VIDIZMO’s Content Embeddings transforms processed content into vector representations that capture semantic meaning, enabling similarity-based search and AI-driven content discovery.
Note: The Embedding App must be enabled for this processing. If disabled, embedding generation and semantic search capabilities are not available.
Content Embeddings Workflow
VIDIZMO provides pre-built graph templates for embedding generation that can be customized in the Workflow Designer. In the Embedding App settings, you select which graph to use for generating content embeddings and which graph to use for vector search operations.
The default embedding workflow processes content through two parallel paths:
Basic Info Path
- Fetch Metadata: Retrieves content metadata including titles, descriptions, tags, and custom attributes.
- Merge Content: Combines metadata fields into unified text blocks for embedding.
- Generate Embeddings: Converts merged metadata into vector representations.
- Store Embeddings: Persists BasicInfo embeddings to the vector database.
Timed Data Path
- Fetch Timed Data: Retrieves time-coded content such as transcripts, captions, video descriptions, and chapters.
- Generate Content Chunks: Splits timed data into semantically coherent segments. Token-aware chunking ensures optimal compatibility with LLMs while preserving timestamp associations.
- Generate Embeddings: Converts each chunk into vector representations.
- Store Embeddings: Persists Timed Data embeddings to the vector database with time references preserved.
Embedding Generation
Content is converted into dense vector representations. Embedding dimensions vary by model (768–3072 dimensions depending on the provider). VIDIZMO supports multiple embedding providers including OpenAI, HuggingFace, Google, and local inference options.
Storage
Embeddings are stored in Elasticsearch, which serves as both the keyword index and vector database. This unified storage enables hybrid search combining vector similarity and keyword matching.
Embedding Outputs Include:
-
Time-coded transcripts
-
OCR-extracted text
-
Video descriptions
-
Image tags and visual attributes
-
Document text and metadata
These outputs are now AI-ready, enabling semantic search, recommendations, and conversational AI interactions.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
The RAG layer leverages embeddings for intelligent content retrieval through portal semantic search and the AI chatbot.
Hybrid Search
VIDIZMO uses a hybrid search combining vector similarity and traditional keyword search:
| Component | Function | What It Finds |
|---|---|---|
| Vector Search | Compares query embeddings with content embeddings | Conceptually related content |
| Keyword Search | Matches exact words or phrases | Content containing specific terms |
Portal Semantic Search
The portal uses hybrid search automatically when the Embedding App is enabled:
-
User enters a search query.
-
Query is converted into an embedding vector.
-
Hybrid search executes across Elasticsearch:
- Vector search surfaces semantically related content.
- Keyword search finds exact matches.
-
Combined results are returned with relevance scores.
Capabilities include concept search, topic discovery, and cross-content search across transcripts, documents, and metadata.
AI Chatbot (RAG)
VIDIZMO's AI Chatbot offers a conversational interface for querying content.
Query Routing
When a user submits a prompt, the LLM first analyzes and classifies the query to determine the appropriate response path:
| Query Type | Routing Decision | Processing Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Content-focused | Prompt requires facts from knowledge base | Vector search retrieves relevant content → LLM generates response with citations |
| General | Prompt requires general knowledge | LLM generates direct answer without content retrieval |
| Web Search | Prompt requires current information | External web search → Results processed by LLM |
| Tool-based | Prompt requires an action | Configured tool is invoked → Results returned to user |
RAG Query Flow
- User Submits Prompt: The chatbot receives a natural language query.
- LLM Classifies Query: The system determines whether the query requires content retrieval, general knowledge, web search, or tool execution.
- Content Retrieval (if needed): For content-focused queries, the system converts the query into an embedding vector and performs hybrid search against the knowledge base.
- Context Assembly: Retrieved content chunks are assembled as context for the LLM.
- Response Generation: The LLM generates a response grounded in the retrieved content, including citations to source materials.
- Response Delivery: The final response is streamed to the user with source references.
Agents and Workflows allow configuration of:
- System prompts and tone
- Knowledge base criteria
- Suggested prompts
- Citation settings
- Branding and interface customization
Search Mashup Tool prioritizes search parameters from:
- Tool Nodes
- Session Context
- LLM suggestions
Summary
VIDIZMO’s content processing and RAG framework converts raw media into an intelligent, searchable knowledge base:
- Content Processing: Extracts transcripts, metadata, and visual insights.
- Content Embeddings: Converts content into semantic vectors for AI-driven search.
- RAG: Powers hybrid semantic search and conversational AI.
Hybrid search ensures content is discoverable via both exact keyword matches and semantic similarity. Organizations can also tune weights to prioritize the most relevant content, making VIDIZMO a powerful platform for knowledge discovery and AI-assisted content management.